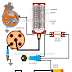
The
diagram illustrates how the diodes rectify the alternating
current flowing in either direction through any two stator winding so that direct current is always available at the output for battery terminal
of the alternator.
Voltage induced in the winding "A" and "C" cause current to flow from the "A" coil of the stator through its positive diode, out of the "Bat" terminal of the alternator and to the battery. The return circuit is from the battery, to the alternator ground terminal, through the negative diode Connected to the "C" coil of the stator and back to the "A" coil where it started, completing the circuit.
Voltage induced in the winding "A" and "C" cause current to flow from the "A" coil of the stator through its positive diode, out of the "Bat" terminal of the alternator and to the battery. The return circuit is from the battery, to the alternator ground terminal, through the negative diode Connected to the "C" coil of the stator and back to the "A" coil where it started, completing the circuit.
DIODE RECTIFIED OUTPUT
When the alternating voltage
induced in these winding is reversed, current will flow out of the "C"
the stator coil of the alternator, through its positive diode, out of the "Bat"
terminal of the alternator and to the battery. This rectified direct current
flows to the battery in the same direction as it did previously. The return
circuit is from the battery, to the alternator ground terminal, through the
negative diode connected to the "A" stator coil and back to the "C"
coil where it started, completing the circuit.
Current flow, in either direction, through the stator winding in the other illustrations can be traced by following the arrows from the stator coil winding, through the positive diode, to the battery, from the battery through the negative diode, through the stator winding back to its source.
These illustrations clearly show that by the action of the diodes, direct current is always flowing into the battery regardless of which stator winding are inducing the voltage or the direction of the current flow through the windings.
Current flow, in either direction, through the stator winding in the other illustrations can be traced by following the arrows from the stator coil winding, through the positive diode, to the battery, from the battery through the negative diode, through the stator winding back to its source.
These illustrations clearly show that by the action of the diodes, direct current is always flowing into the battery regardless of which stator winding are inducing the voltage or the direction of the current flow through the windings.






0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.