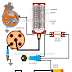
By using a hydrometer, the specific gravity of the electrolyte solution in a battery can be determined. The battery specific gravity is an indication of the battery state of charge. If the state of charge is low, the hydrometer will read low. If the state of charge is high, the hydrometer will read high. As an example, a reading from 1.260 to 1.280 indicates a fully-charged battery. A reading from 1.200 indicates a battery is in a discharged condition and cannot give satisfactory service.
The definition of specific gravity is the weight of the liquid compared to the weight of an equal volume of water. The specific gravity of chemically pure water at 80°F. is “one”. Therefore, by knowing the specific gravity of sulphuric acid, we can accurately measure the ratio of sulphuric acid to water in the battery electrolyte solution.
As a battery becomes discharged, a portion of the acid in the solution, becomes
soaked into the plates, so to speak. This leaves the solution with a weaker
acid content and consequently in a weaker state of specific gravity. When
the battery is recharged, the acid is driven from the plates back into the
solution, restoring the solution and the specific gravity to full
strength. The hydrometer reading indicates either of these conditions thereby
revealing the battery state of charge.
After activating a dry-charge battery, check the specific gravity. The gravity
reading should be 1.260 or slightly higher. If the electrolyte level drops
shortly after the initial fill, due to the plates and separators absorbing some
of the solution, add more electrolyte to bring the solution up to the proper
level. When so instructed, charge the battery at 15 amperes for 10 minutes
before installing the battery to assure a full charge.








0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.