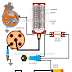
The ignition system is employed to generate a very high voltage (from 18 to 30 thousand volts) to jump across the spark plug gap to ignite the air-fuel mixture inside the combustion chamber of a gasoline engine.The ignition system consist of two main circuits.
1. PRIMARY CIRCUIT:
Primary circuit is also called the low voltage or the low tension circuit. This is the circuit through which current flows at battery or generator voltage. The ignition switch, resistor, ignition coil primary winding, breaker points and the condenser are all in the primary circuit.
2. SECONDARY CIRCUIT:
The
secondary ignition circuit is also called the high voltage or high tension
circuit. The coil secondary winding, distributor rotor, distributor cap, high
tension leads, and the spark plugs are all part of the secondary circuit.
THE IGNITION SYSTEM
HOW IGNITION SYSTEM WORKS:
The
primary ballast resister is essentially a current compensating device
consisting of a resistor unit or wire located in the primary ignition circuit. The
compensating action is obtained because, at low engine speeds, the current
flows for longer period of time. This heats up the resistor, thereby raising
its resistance and reducing current flow. This action serves to keep the coil
primary winding cooler and improves distributor breaker point life. At high
speeds, the current flows for shorter periods of time which lets the resistor
cool and increases the current flow in the primary winding of the coil. This action
permits maximum secondary voltage to be obtained.
Because of the lowered battery voltage resulting from the starter load on some vehicles, the ballast resister is bypassed while the starting system is in operation. This is done to provide higher secondary voltage for starting.






0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.